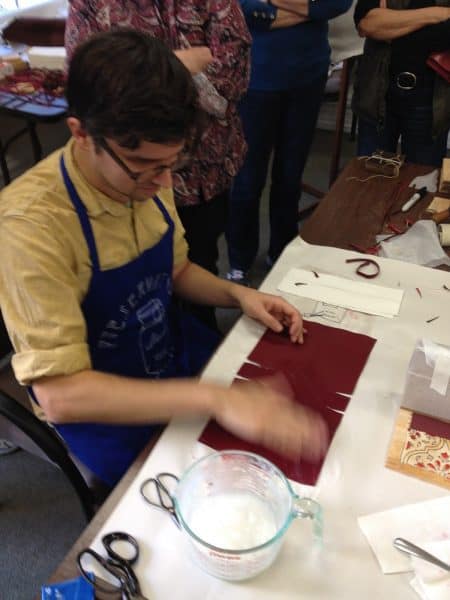
Over the weekend of October 25th and 26th, the Library Company was the host site for a workshop on Ethiopian Bookbinding that was sponsored by the Delaware Valley Chapter of the Guild of Book Workers. The Library Company conservators are all members or officers of the chapter and have organized a number of guild events over the years. Ten students attended the workshop, which was taught by Bill Hanscom, a conservation technician for special collections at Harvard Library. Bill has been researching Ethiopian bookbinding for a while and is currently writing an essay to be published in the next volume of Suave Mechanicals: Essays on the History of Bookbinding.
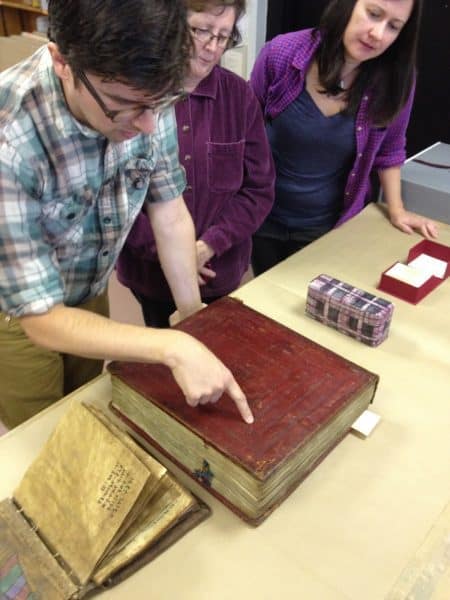

At the beginning of the workshop, Bill showed images of Ethiopian bindings and explained the typical features. Amazingly, many of the features have not changed for more than 1400 years. He showed some videos of the books being made in a marketplace in Ethiopia. In one video, a man was squatting and working on the ground, applying paste to the covering leather with his hand. Next, our group examined two Ethiopian bindings owned by the Library Company, one rather large and grand and the other very modest, almost primitive. In the past, I always thought they were interesting bindings. But now that I knew more about how they were made and could identify the various features, I looked at them with new eyes! It was very helpful for everyone to be able to examine authentic examples.
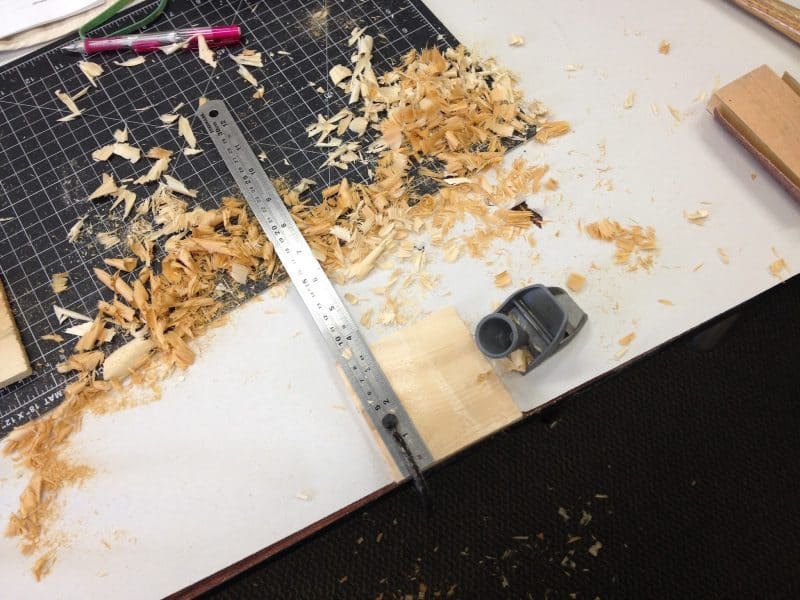

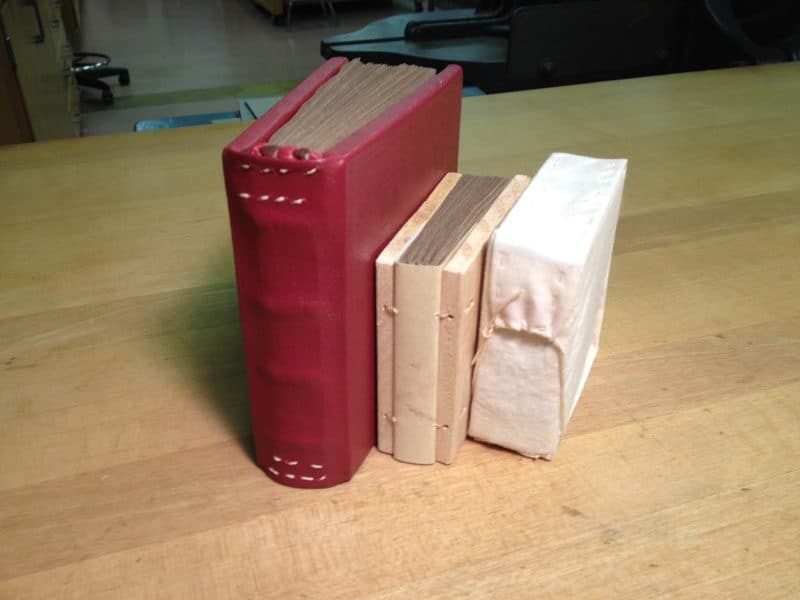
Then we started working on our own historically accurate models. We shaped and pierced wooden boards. We made sewing “thread” buy cutting a thin spiral out of a circle of parchment, and then moistening and twisting it into one long strand. Most of us made three books, one covered in leather, one with a cloth wrapper called a “lebas,” and one with a parchment spine.
Today, Ethiopian bindings are still made with only a few tools. Unlike the man in the video, we worked sitting at tables, but tried to follow his technique otherwise. For me, it is always inspirational to make a historical model. I try to imagine how various binding features evolved over time and to consider their purpose. Was it structure, decoration, or tradition? In many cases it could be all three. But the most important thing is that it helps me know what I am looking at and what is important when I approach a binding in my work as a conservator.
Jennifer Rosner
Chief of Conservation
The Library Company of Philadelphia
1314 Locust St., Philadelphia, PA 19107
TEL 215-546-3181 FAX 215-546-5167









